"Dry Eye" syndrome treatment
What is "Dry Eye" syndrome
Dry eye syndrome is a chronic and usually progressive condition. In most cases, dry eyes can be successfully mitigated, which usually results in significantly greater comfort in the eyes, fewer symptoms of dryness, and sometimes even better vision.
Dry eyes are caused by a lack of adequate tears. Tears are a complex mixture of water, fat and mucus. This mixture makes the surface of the eyes smooth and clear and protects the eyes from infections. The main part of the tears is water, and the rest is composed of other inorganic substances: sodium chloride, sodium carbonate, magnesium carbonate and calcium. Tears contain proteins and carbohydrates.
For some people, the cause of dry eyes is reduced tear production. For others, it is increased evaporation of tears and imbalance in their composition. It has been found that in over 85% of dry eyes cases the problem is in the lipid layer of the tears, which is produced by the meibomian glands in the eyelids.
Tear film
The tear film plays one of the most important roles by keeping the eyes moist, cleansing the eye surface and providing protection against injury and infection. By blinking the eyelids, the film spreads evenly, which usually happens every 10 seconds. The tear film has three distinct layers, each of which performs a specific function:
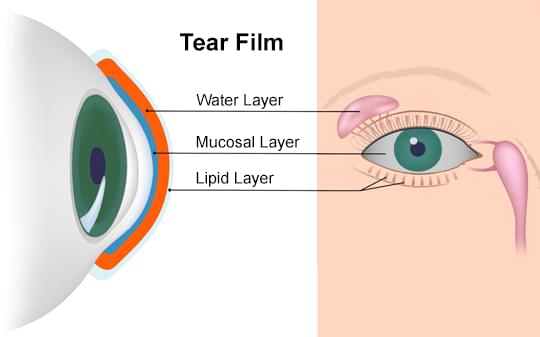
Water layer
The aqueous (water) layer makes up 90% of the volume of the tear film and is produced by the lacrimal glands. It supplies the corneal epithelium with nutrients and atmospheric oxygen and has an antibacterial effect. It also cleans the eye surface by washing away accumulated particles and bacteria.
Mucosal layer
The innermost layer of the tear film consists of mucus, which is produced by the conjunctiva. It covers the surface of the cornea and significantly reduces the pressure on the ocular surface. In addition, it allows easy and even spreading of the water layer on the cornea, which is important for visual acuity.
Lipid layer
The lipid (oil) layer forms the outermost surface of the tear film and is produced by the meibomian glands. Its main function is to protect the intraocular fluid from evaporation. In addition, it prevents the overflow of tears from the eye and stabilizes the tear film. The most common cause of dry eye is a problem in the lipid layer due to impaired function of the meibomian glands (over 85%).
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms that usually affect both eyes may include:
- Burning sensation in the eyes
- Thick secretions in or around the eyes
- Sensitivity to light
- Redness of the eyes
- Sensation of a foreign body in the eyes
- Difficulty driving at night
- Watery, very moist eyes, which is the body's response to irritation from dry eyes
- Blurred vision or tired eyes
- Difficult to wear contact lenses
Risk factors
- Age /production of tears reduces with age, as one third of people over 40 years suffer from dry eye syndrome/
- Hormonal changes /more common in women due to the use of birth control pills or menopause /
- Prolonged wearing of contact lenses
- Eating a diet low in omega-3 fatty acids
- Adverse environmental factors - air conditioners, cigarette smoke, dry air
- Reduced blinking /long work in front of screens or prolonged driving/
- Eye diseases - blepharitis, allergies, infections
- Preservatives in eye drops /in the treatment of eye diseases/
Diagnostics of dry eye
In over 85% of dry eyes cases, the cause is a problem in the lipid layer of tears, which is produced by the meibomian glands in the eyelids. Therefore, the diagnosis of dry eye is mainly aimed at assessing the anatomy and function of the meibomian glands. The test is called a meibography and is performed with special diagnostic devices, some of which can monitor additional parameters in case of dry eye (tear breakup time, tear meniscus height, quantitative and qualitative assessment of the lipid layer). The test is recommended for objective proof of dry eye, as well as after completing a course of four photobiomodulation procedures (type of phototherapy). Meibography can be used to monitor the healing effects of phototherapy or simply to monitor the development of dry eye disease over time without treatment.
Diagnostics of dry eye with Antares (by Lumenis)
- accurate, reliable and repeatable results
- fast research and data processing
- comfort for the patient and the doctor
- many uses:
- report for dry eye
- Meibography
- tear film breakup time
- height of the tear meniscus
- topographer

Treatment of dry eye
Replacing the insufficient natural tears with artificial ones is the most commonly practiced treatment. Artificial tears are available without a prescription and are used in the form of drops (standard) or gel (in severe cases), providing the necessary lubrication to the eye. They are usually applied several times a day and can be used much more often, depending on the patient's needs. Such treatment is a substitutional, and when the artificial tears are stopped, the symptoms of dry eye will reappear.
Preserving naturally produced tears is another method of maintaining moisture in the eyes. Normally, tears flow through the lacrimal ducts of the upper and lower eyelids to the lacrimal sac. It is possible to place temporary "plugs" on the tear ducts in order to stop the drainage of tears. This procedure is performed only as a last resort, due to the risk of tear discharge with slightly to moderately reduced tear secretion. Periodic replacement of the "plugs" according to the manufacturer's instructions is also required.
Modern treatment of dry eye includes stimulation of the meibomian glands in order to normalize their function that would result in recovery of the lipid layer of human tears. To this end, nutritional supplements, cleansing hygiene procedures and specifically targeted phototherapy have been developed, the latter playing a key role in mitigating the symptoms of dry eye.
Photobiomodulation
Photobiomodulation (a type of phototherapy) is a procedure in which the meibomian glands in the eyelids are irradiated. The technology is based on the action of IPL-based devices, widely used in dermatology for decades for aesthetic purposes. Some dermatologists report that in addition to the desired photo-rejuvenating effect on the facial skin, their patients also report relief of dry eye symptoms.
Subsequently, the devices are modified, and specific eye use protocols are developed. When the technology is applied on the eyelids, the morphologically changed meibomian glands are revitalized, which normalizes the secretion and increases the quality of the lipid component of the tear film. In addition to its healing effect, photobiomodulation has an aesthetic effect - it stimulates the synthesis of collagen in the skin and slows down its aging.
Photobiomodulation with OptiLight (by Lumenis)
Lumenis, the inventor of IPL technology, provides to ophthalmologists the first and only FDA-approved device for the treatment of dry eye. The principle of action is phototherapy (photobiomodulation) through the patented Lumenis technology - OPT (Optimal Pulse Technology).
The OptiLight procedure is a safe, precise and elegant solution to the problem of dry eye syndrome.
How it works
Photobiomodulation with OptiLight stops the pathological inflammatory cycle in dry eye
- Proven to reduce mediators of inflammation
- Restores the morphology and function of the meibomian glands
- Significantly improves the tear breakup time
- Destroys abnormal blood vessels that support the inflammatory response
- Reduces the population of demodex micelles, which stimulate the inflammatory response and facilitate bacterial growth on the eyelids
Advantages of photobiomodulation with OptiLight
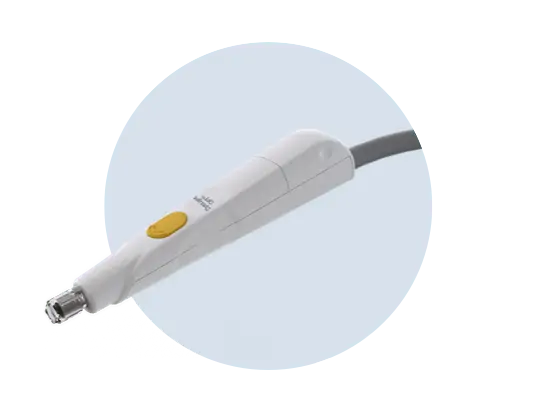

Patented handpiece with Optimal Pulse Technology (OPT) - follows individually even the most delicate contours and curves of the face

Second handpiece with IPL technology (SapphireCool ™ technology) with specially designed ergonomic design for the needs of ophthalmologists in the treatment of dry eye
Established treatment protocols with the possibility of specific adjustments according to the degree of damage and the needs of the patient

OPT (Optimal Pulse Technology) - precise and effective treatment through optimal energy distribution during the procedure - the future of phototherapy for dry eye
Indications for photobiomodulation
Although patients with dry eye feel relief after the first photobiomodulation procedure, the recommended course of treatment is 4 procedures at intervals of 2-3 weeks. To maintain the effect over time, a maintenance procedure is recommended once a year, and in more severe cases of dry eye, this period can be shortened to half or even a quarter of a year. Warming masks are often applied to the eyelids after photobiomodulation procedure, which facilitates the expression of the secretion of the meibomian glands. For maximum effect in the treatment of dry eye, the warming mask can be replaced with subsequent photobiostimulation (another type of phototherapy).
In addition to dry to dry eye photobiomodulation can be used for non-surgical treatment of stye. While in the acute stage of the disease only 2 procedures are sufficient, in the chronic phase the whole course of treatment of 4 procedures is required.
photobiostimulation
Photobiostimulation is a type of LLLT phototherapy (Low Level Light Therapy) in which an LED source emits light on the skin. Light photons of a certain wavelength are absorbed by the corresponding cellular components (partially mitochondria), triggering a cascade of biochemical processes:
- Red light (633nm) - reduces inflammatory reactions, pigmentation and redness, improving cell regenerative capacity and skin microcirculation
- Near-infrared light (830nm) - reaches deeper fibroblast cells, stimulating the production of collagen and elastin for healthier and younger skin.
- Blue light (415nm) - neutralizes bacteria that cause redness and inflammation in acne. It is mainly used in dermatology.
Photobiostimulation with Omnilux Contour
The photostimulation with the Omnilux Contour mask combines the healing effect of red light and the aesthetic impact of near-infrared light:
Antimicrobial action
Reduces the population of bacteria and parasites on the eyelids and eyelashes. Demodex folliculorum (an ectoparasite living in hair follicles and sebaceous glands) and Bacillus olerinus have been found to play a key role in the etiology of blepharitic changes and meibomian gland dysfunction.
Anti-inflammatory action
Тhe inflammatory reaction is a proven pathogenetic mechanism for the development and progression of dry eye. The levels of inflammatory mediators (cytokines, matrix metalloproteinases and chemokines) in the tears of patients with dry eye is greatly increased compared to healthy patients.
Antioxidant effect
Irradiation of the eyelids increases the levels of ATP in the meibomian glands, which improves their function and reduces the symptoms of dry eye (normalizes the lipid component of the tear film).
Aesthetic effect on the skin is achieved through increased synthesis of collagen and elastin due to fibroblast activity and modulation of cytokines.
Accelerated recovery processes
Increased cellular metabolism and increased production of ATP contribute to the rapid reduction of postoperative edema.
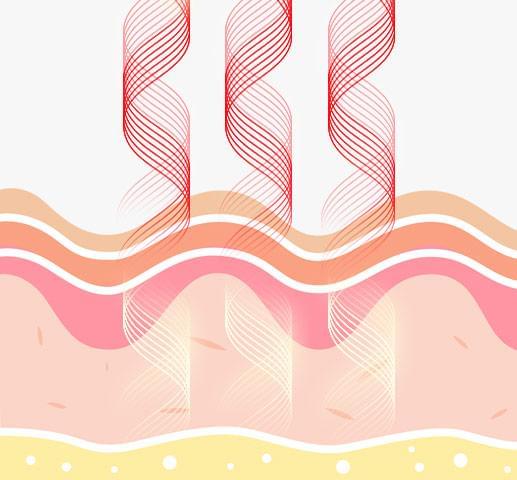

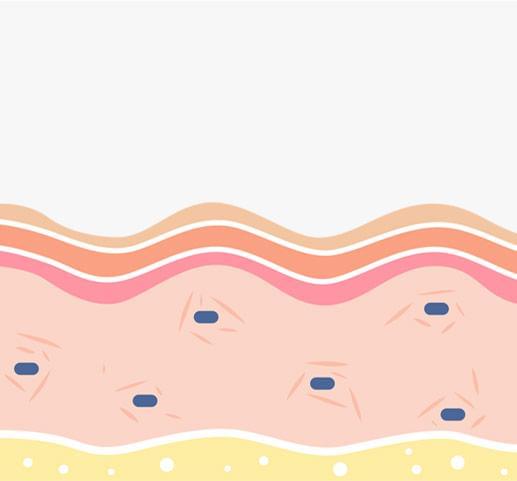
Visible red and near-infrared light is absorbed into the skin and the dermis.
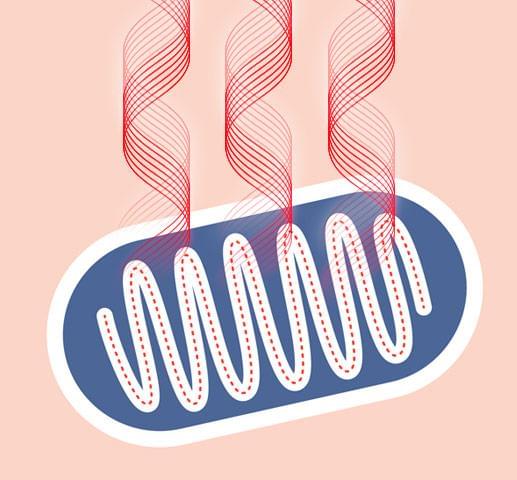
Mitochondria (the cell's "battery") absorbs the light and converts it to energy for cellular activity.
Increased cellular activity produces a cascade of reactions called secondary reactions.
Secondary reactions include the increased production of collagen (called collagenisis) and elastin.
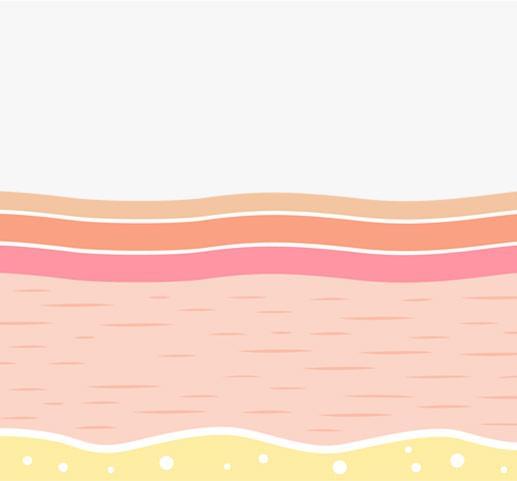
New collagen forms within the dermis, resulting in plumper, smoother and more radiant skin.

Advantages of photobiostimulation with Omnilux Contour
- non-invasive and painless procedure
- safe procedure for all skin types
- fast and comfortable procedure
- proven results
Indications for photobiostimulation
Photobiostimulation can be applied as a supplementary procedure after photobiomodulation to achieve maximum effect in the treatment of dry eye. It is also indicated as a individual treatment after completing a course of 4 photobiomodulation procedures. 2 procedures per week for a period of at least 1 month are recommended.
The procedure can be used after eyelid interventions, most often after surgical blepharoplasty, in order to shorten the recovery period and reduce postoperative edema. The recommended application is 2 procedures until the end of the first week after the manipulation. The Omnilux Contour mask can be used for purely aesthetic purposes to photorejuvenate facial skin for a long period of time (3 times a week for at least 1 month).
Blepharoexfoliation with AB Max
Blepharoexfoliation is a procedure to remove accumulated dirt and debris (waste substances) from the eyelashes of the eyelids, which reduces the number of pathogenic bacteria. It is indicated for blepharitis and/ or dry eye, when patients cannot do the cleansing at home with standard hygiene solutions.
An interval of about 4-6 months between procedures is recommended, and it can be adapted to individual needs. AB Max is a high-tech system for blepharoexfoliation (Distal-Ciliary Cleansing System) with the ability to work in two directions or in a patented pulse mode.
